How to connect Amazon RDS with Instances: EC2 and Local Instances
Posted By :Harsh Kumar |24th November 2020
As we are all aware that Databases are software that can manage and store your data. Similarly, if we want to manage our SQL data or relational data then AWS Relational Database Service (RDS) comes into the picture. So, AWS RDS is not a database instead it is a service using which you can use various databases, for example, MySQL, Aurora, Postgres, and other RDBS.
Benefits for AWS RDS:
- This service manages your automatic backup.
- It manages all the security patches.
- It runs on AWS, so it is very much reliable.
- With just a few clicks, you can resize the compute and storage.
Now let us know how to create a MySQL database using RDS.
Creating a MySQL database in RDS:
Step1. Sign-in to AWS console and go to the RDS service page
Step2. Click on create a database.
Step3. Choose MySQL from the given options
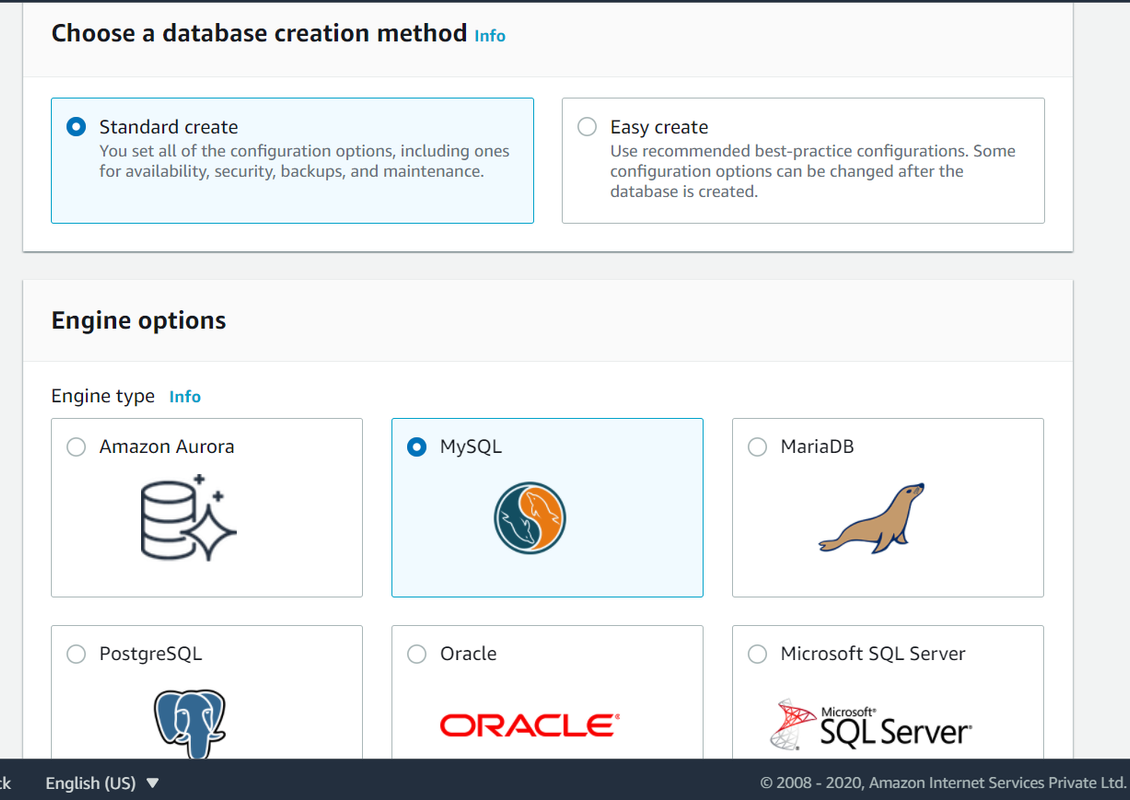
Step4. Fill in other details for your database like the template, username, password, instance size, storage, etc, and click Create database at the bottom.
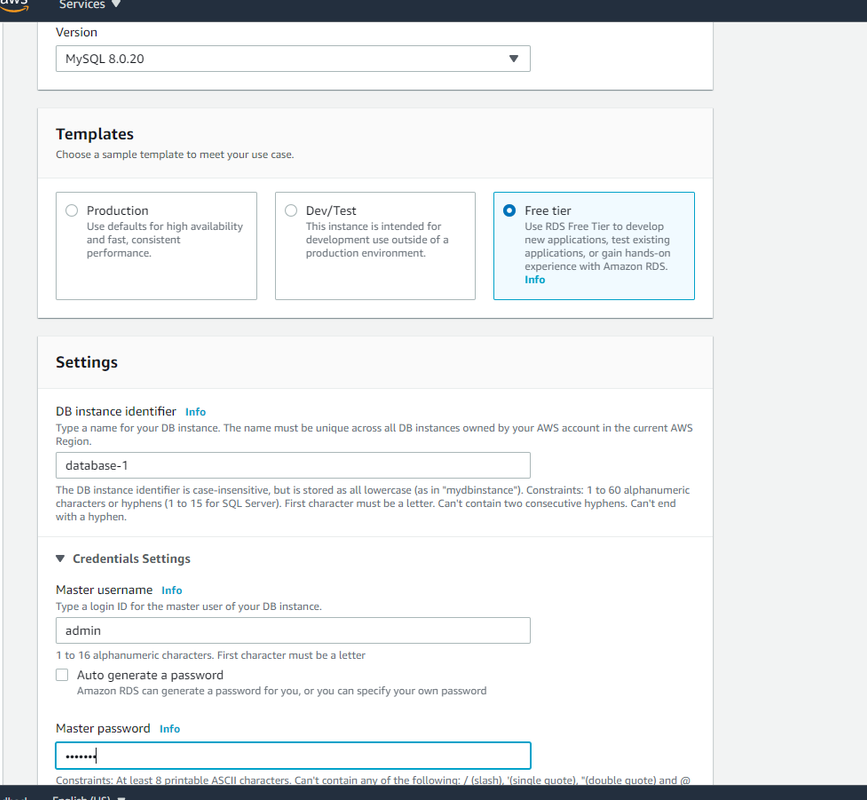
Then you will get the RDS instance details after the database gets created.
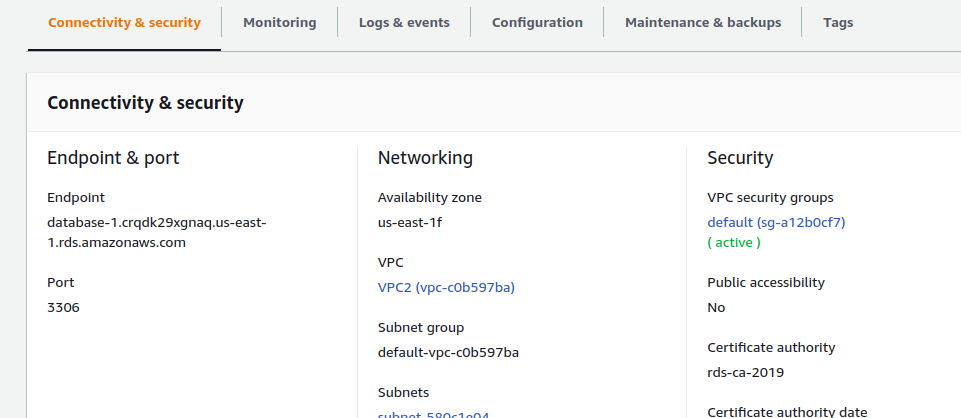
Connect RDS with EC2 instance (Linux).
To connect RDS with EC2, we need to create an EC2 with considering some important points like
- EC2 should be in the same network (VPC peering will be used for different networks).
- EC2 should have mysql-client installed to connect with the RDS database.
Step1. Create an EC2 instance (in this case Ubuntu).
Step2. Install mysql-client in EC2 instance
$ sudo apt-get install mysql-client
Step3. Add EC2 instance IP or EC2 instance security group in the RDS instance security group.
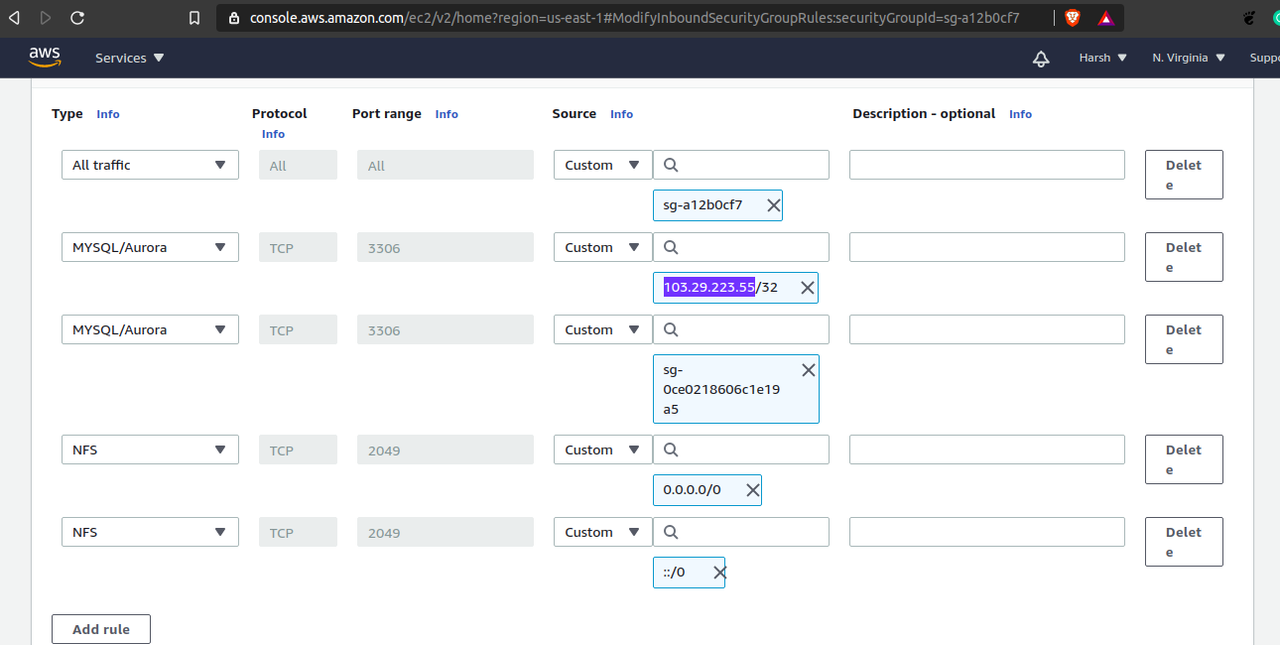
Step4. Now connect to MySQL database using RDS Endpoint.
$ mysql -h <rds-endpoint> -P 3306 -u username -p
Then enter the password and start using the database.
Connect RDS with Local instance.
There are two methods to connect local instance or system to AWS RDS:
- SSH tunneling
- Public access to RDS.
In this case 2nd method i.e. Public access of RDS has been demonstrated.
Note: This method is not for production use. Use this method only for learning purposes.
Step1. Go to your RDS instance and click on modify instance at the top right.
Step2. Now choose “Publicly accessible” in Connectivity.
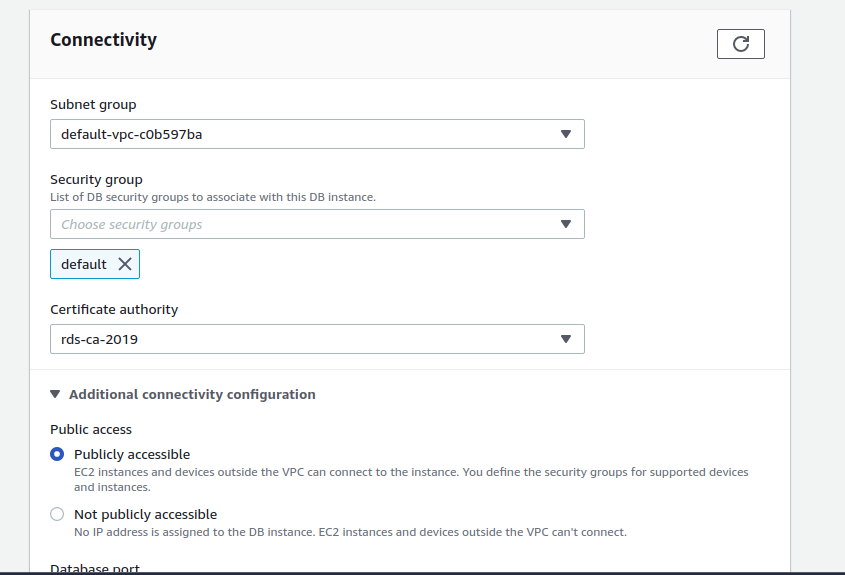
Step3. Now add your local instance public IP address in the RDS security group.

Step4. Now install mysql-client on your local instance.
$ sudo apt-get install mysql-client
Step5. Try to connect to the MySQL database of RDS.
$ mysql -h <rds-endpoint> -P 3306 -u username -p
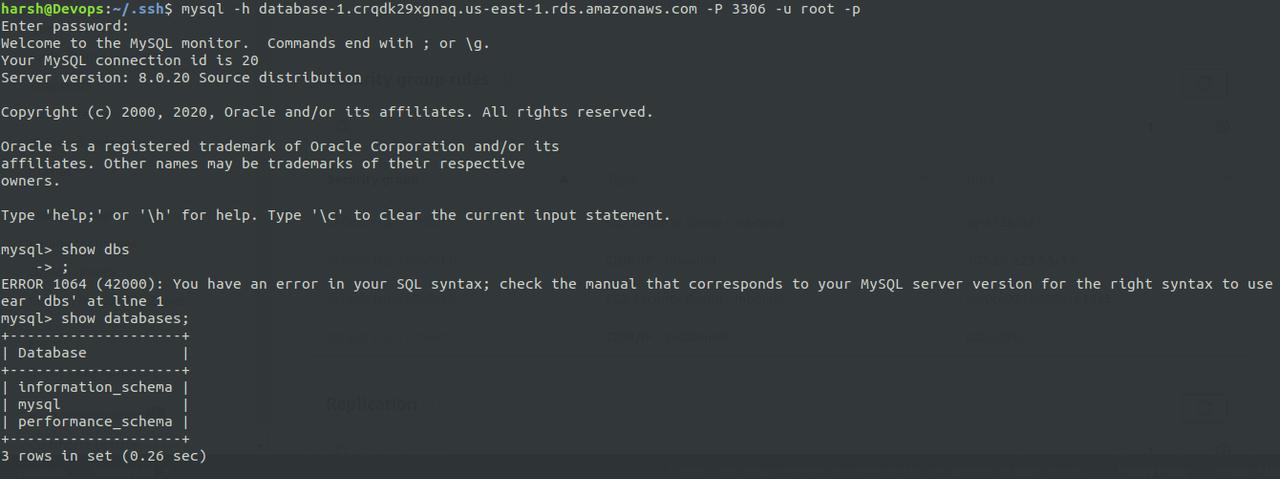
Now use the RDS database in your local instance.



